Project B1
T cells as regulative element during the onset of autoantibody-mediated arthritis
Our published data from the first funding period of PANDORA identified tissue-resident antiinflammatory Cx3cr1+ macrophages that form protective barriers around synovial joints and prevent onset of autoantibody-mediated joint inflammation under homeostatic conditions. Our preliminary data show that autoreactive T cells interact with such barrier-forming synovial Cx3cr1+ macrophages prior to onset of inflammation thereby lowering the local inflammatory threshold and “licensing” the synovial tissue for autoantibody-induced arthritis via production of granulocytemacrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF). During the second funding period, we thus seek to decipher the GM-CSF-dependent molecular mechanisms and responding synovial cell types that enable onset of autoantibody-induced arthritis and additionally plan to determine the relevance of the underlying processes for human RA.
2019-2022 (1st funding period):
Checkpoints and mechanisms that control the onset of autoantibody-mediated inflammatory diseases such as RA remain incompletely understood. Our preliminary data show that collagen II (CII)-specific autoreactive T cells essentially control the onset of arthritis that develops upon passive transfer of CII-specific arthritogenic autoantibodies. Although underlying molecular mechanisms remain elusive, our preliminary findings suggest that autoreactive IL-23-dependent T cells “license” the joint for autoantibody-induced inflammation and that T cells and autoantibodies act in a synergistic and antigen-specific manner.
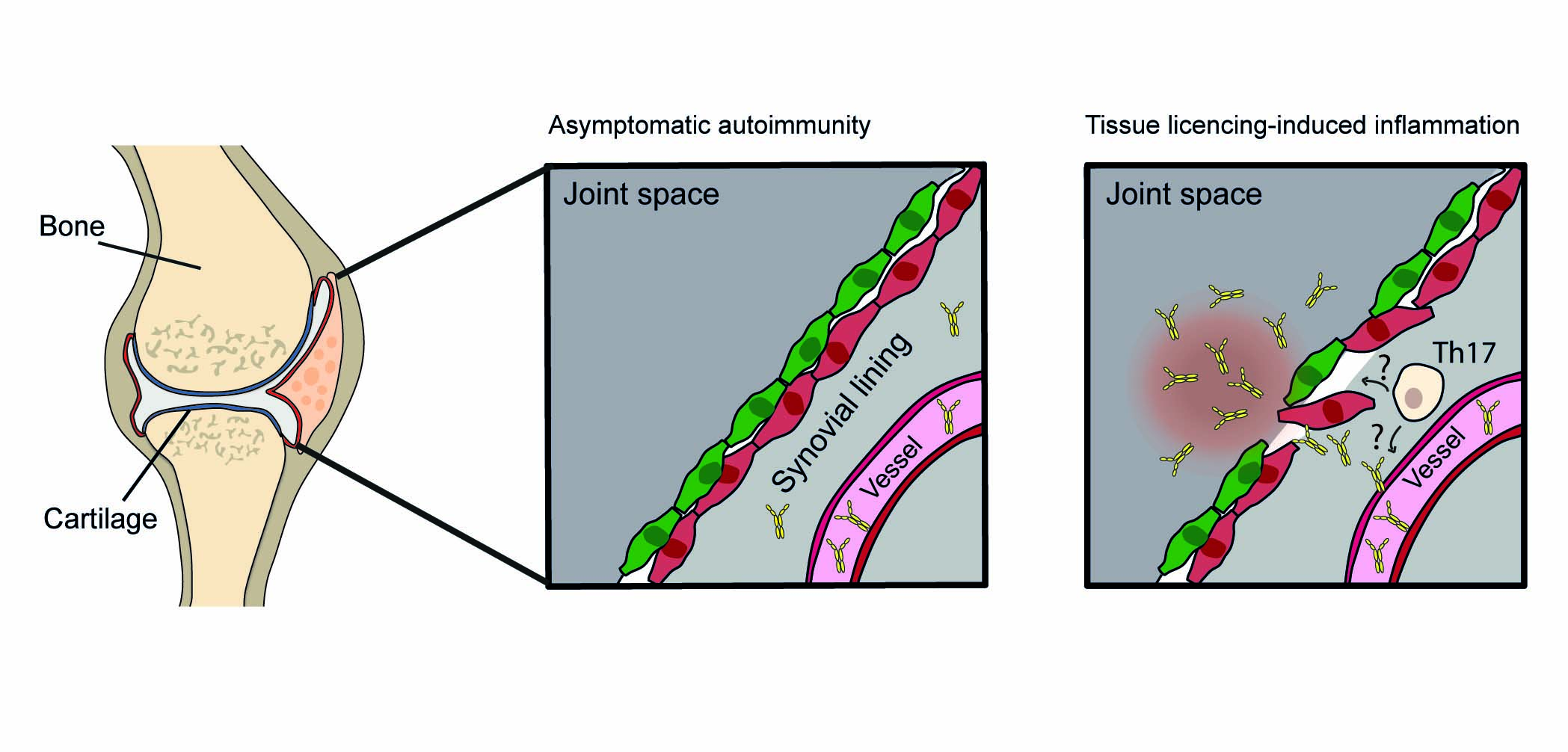
The aim of this project is to dissect and understand underlying events and in particular to address a role of specific T cell subsets in regulating the trafficking and activity of autoantibodies to and within the joint as well as to determine the relevance of this phenomenon for human RA.
Prof. Dr. med. Gerhard Krönke
Department of Medicine 3
Chair of Medicine III (Prof. Dr. Schett)
- Phone number: +49 9131 85-34742
- Email: gerhard.kroenke@uk-erlangen.de
Dr. rer. nat. Rene Pfeifle
Department of Medicine 3
Chair of Medicine III (Prof. Dr. Schett)
- Phone number: 0913185-2913185-39352
- Email: rene.pfleifle@uk-erlangen.de
Alexandra Klej
Department of Medicine 3
Chair of Medicine III (Prof. Dr. Schett)
- Phone number: +49 9131 85-39107
- Email: alexandra.klej@uk-erlangen.de



